Galvanizing plants play a crucial role in various industries by providing a robust layer of protection for steel and iron products. This process, known as galvanization, involves coating metal with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of the product. Understanding the science behind galvanizing plants reveals the importance of this process and how it significantly impacts the durability and performance of metal products.
The Galvanizing Process
The galvanizing process can be, broken down into several key stages: surface preparation, galvanization, and finishing. Each stage is essential to ensure a uniform, high-quality zinc coating that provides maximum protection against corrosion.
1. Surface Preparation
Before the galvanization can begin, the metal surface must be, thoroughly cleaned to ensure proper adhesion of the zinc coating. This preparation involves three main steps: degreasing, pickling, and fluxing.
- Degreasing: The metal is, cleaned to remove any grease, oil, dirt, or other contaminants that may interfere with the galvanization process. This step often involves an alkaline or acid-based solution.
- Pickling: After degreasing, the metal is, immersed in an acidic solution (usually hydrochloric or sulfuric acid) to remove any rust, scale, or oxide layers. This step ensures the surface is free of impurities that could prevent the zinc from bonding properly.
- Fluxing: The final step in surface preparation involves applying a flux solution, which typically contains zinc ammonium chloride and zinc dust. This solution further cleans the metal surface and prevents oxidation before the galvanization process.
2. Galvanization
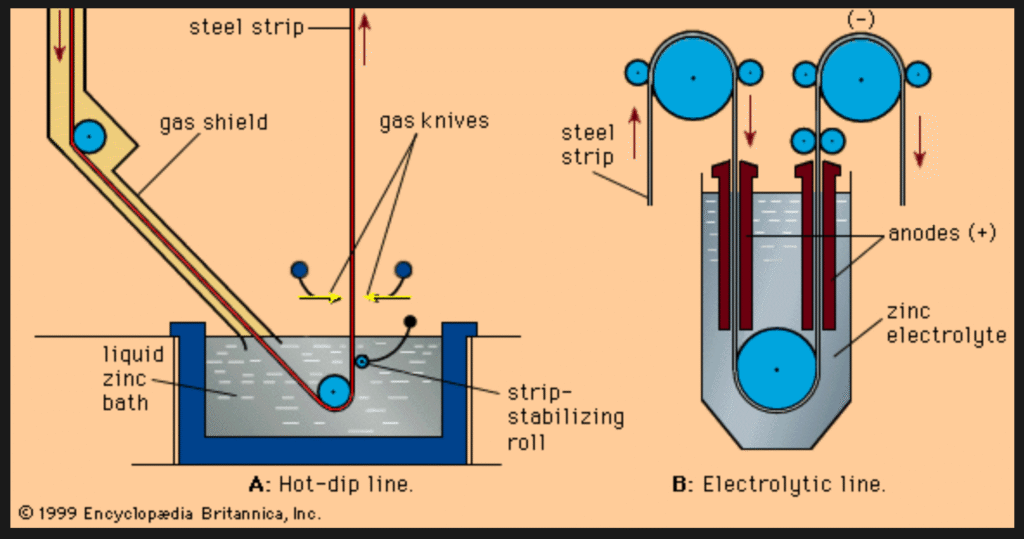
Once the metal surface is, properly prepared, the actual galvanization process can begin. This involves immersing the cleaned metal into a bath of molten zinc, which is, typically maintained at a temperature of around 450°C (842°F). The metal remains in the zinc bath until it reaches the same temperature as the molten zinc, ensuring a thorough coating.
During immersion, a metallurgical reaction occurs between the iron in the steel and the molten zinc. This reaction forms a series of zinc-iron alloy layers on the metal’s surface, with an outer layer of pure zinc. These layers create a robust and durable coating that provides exceptional protection against corrosion.
3. Finishing
After the metal is, removed from the zinc bath, it undergoes a series of finishing steps to ensure the quality and appearance of the galvanized coating. These steps may include quenching, inspection, and post-galvanizing treatments.
- Quenching: The galvanized metal is, often quenched in a solution of water and chemicals to cool it rapidly and prevent the formation of excessive zinc-iron alloy layers. This step also helps to passivate the surface and enhance the coating’s appearance.
- Inspection: Quality control is crucial in the galvanizing process. The galvanized metal is, inspected for uniformity, thickness, and any defects that may affect its performance. This inspection may involve visual checks, coating thickness measurements, and adhesion tests.
- Post-Galvanizing Treatments: Additional treatments may be, applied to enhance the performance and appearance of the galvanized coating. These treatments can include chromating, phosphating, or painting, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
The Importance of Galvanizing Plants
Galvanizing plants are vital to various industries, including construction, automotive, agriculture, and infrastructure. The benefits of galvanization extend beyond mere corrosion protection, offering several key advantages:
1. Enhanced Durability
Galvanized coatings provide long-lasting protection against corrosion, significantly extending the lifespan of steel and iron products. This durability reduces the need for frequent maintenance and replacement, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
2. Cost-Effective Solution
Compared to other corrosion protection methods, galvanization is relatively inexpensive. The initial investment in galvanizing plants and processes is, offset by the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance and replacement costs.
3. Versatility
Galvanizing is suitable for a wide range of applications, from small fasteners to large structural components. The process can be, adapted to various shapes, sizes, and thicknesses, making it a versatile solution for many industries.
4. Environmental Benefits
Galvanization is an environmentally friendly process. Zinc is a natural, abundant element that can be, recycled without losing its properties. Additionally, the extended lifespan of galvanized products reduces the demand for raw materials and energy, contributing to sustainability efforts.
5. Reliable Performance
Galvanized coatings provide consistent and reliable performance, even in harsh environments. The robust protection against corrosion ensures that products can withstand exposure to moisture, chemicals, and other corrosive elements.
Conclusion
The science behind galvanizing plants underscores their critical role in enhancing the durability and performance of metal products. By understanding the galvanizing process and its benefits, industries can make informed decisions about corrosion protection and ensure the longevity of their steel and iron components. As a cost-effective, versatile, and environmentally friendly solution, galvanization continues to be a cornerstone of modern manufacturing and construction practices.